C3PO: Canonicalization of 3D Pose from Partial Views with Generalizable Correspondence Features
A novel, optimal-transport based learning method to solve the challenge of matching semantically similar parts distinguished by their geometric properties, e.g., left/right eyes or front/back legs. It is faster and outperforms previous supervised methods in terms of semantic matching and geometric understanding.
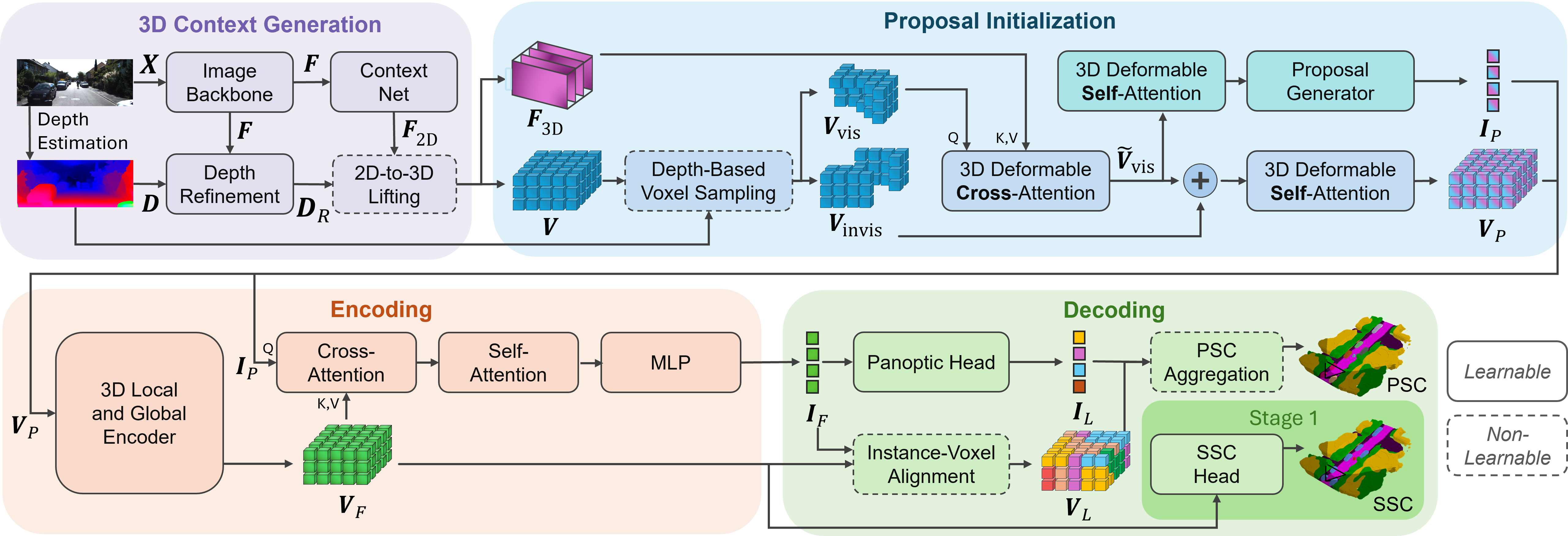
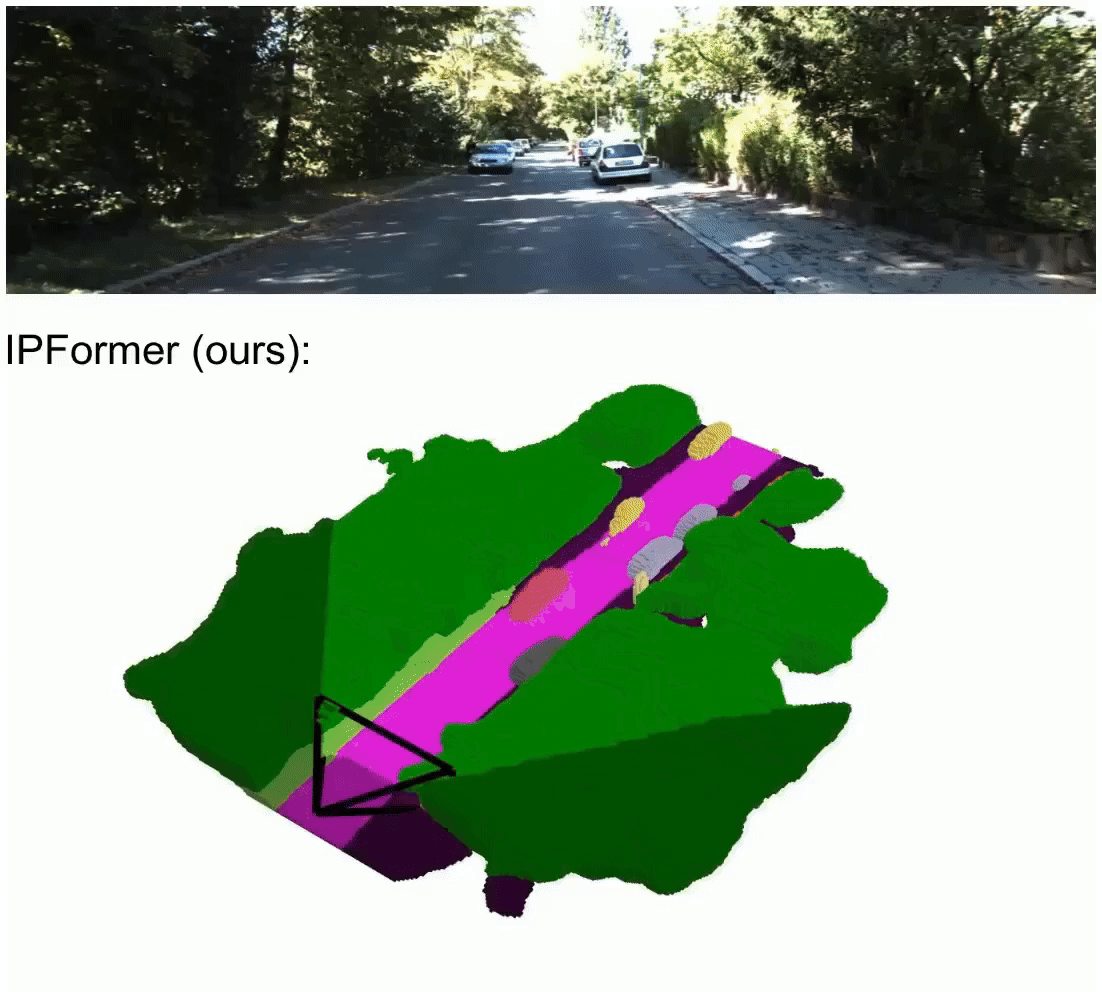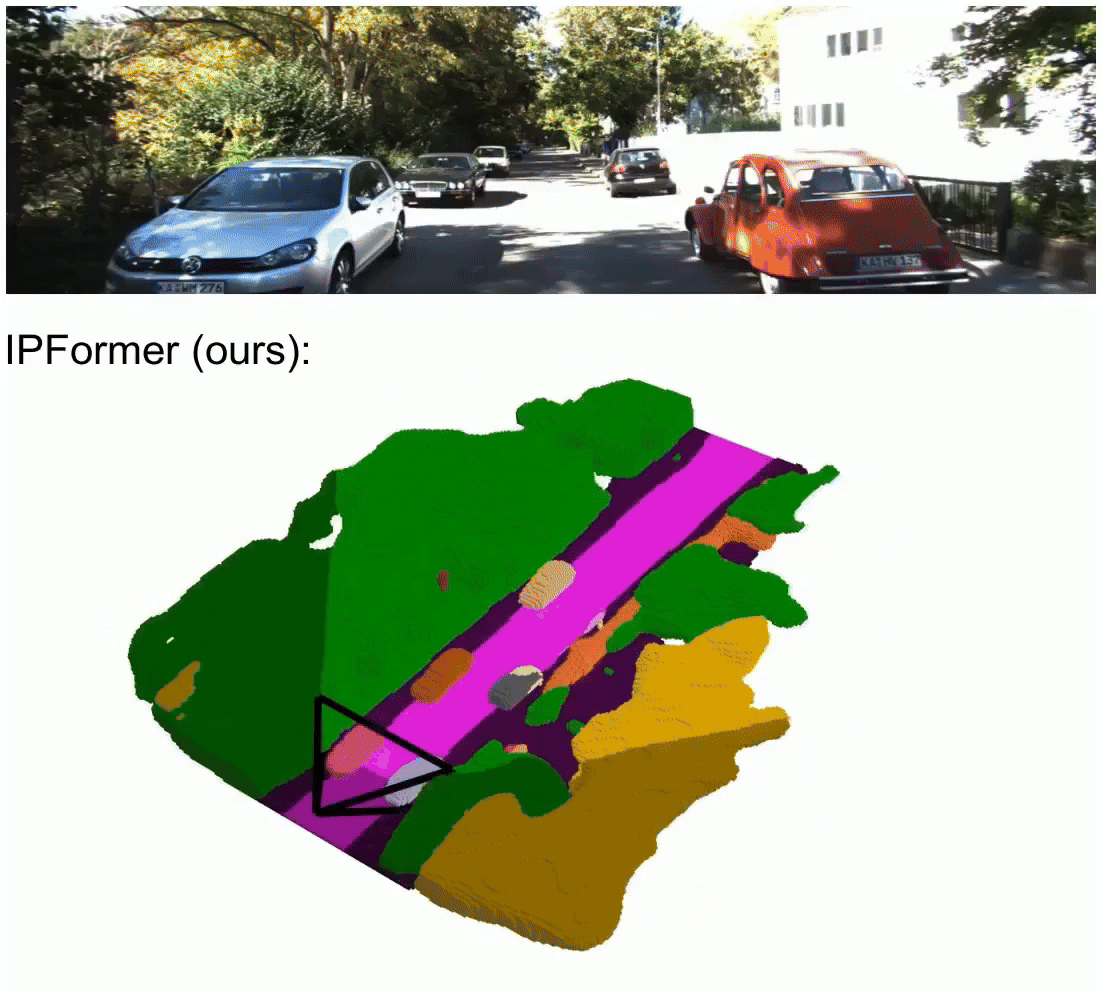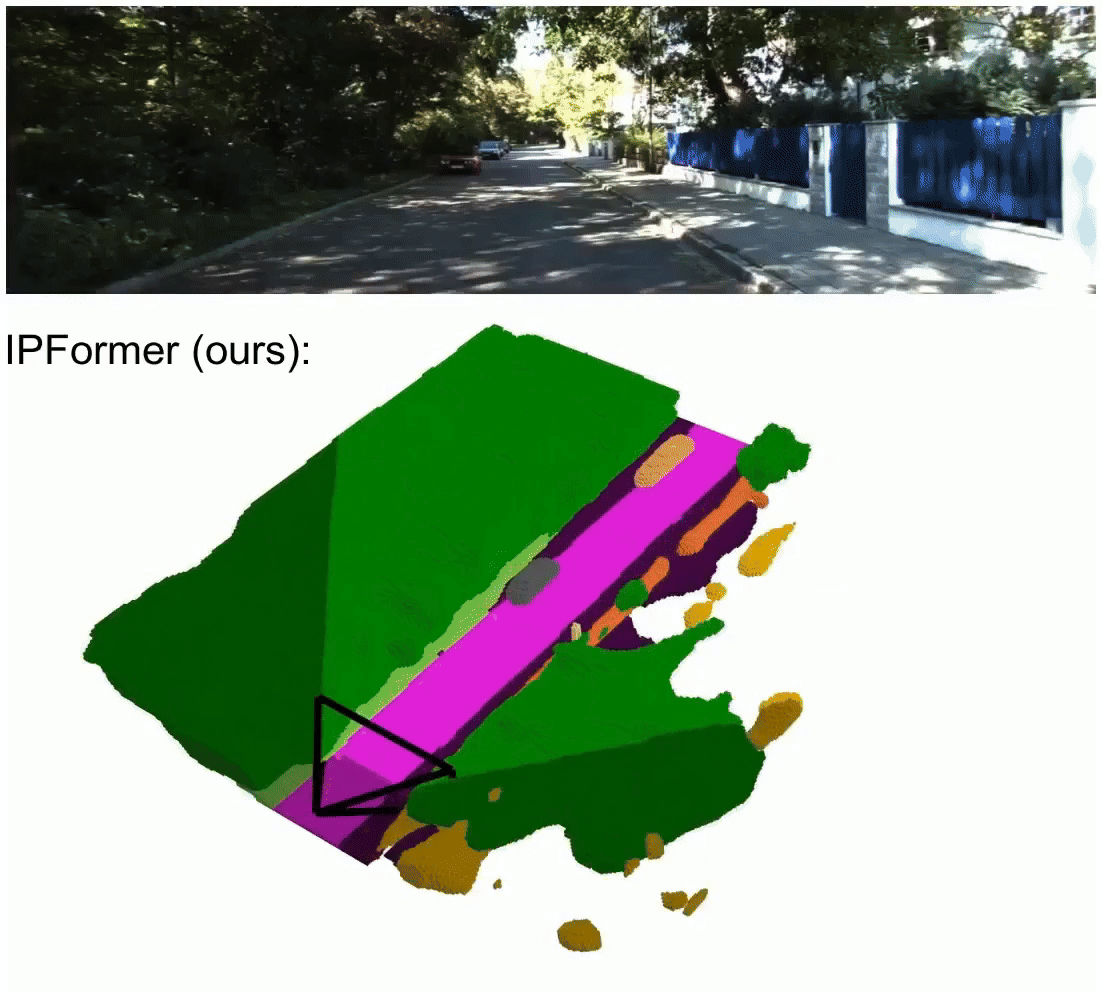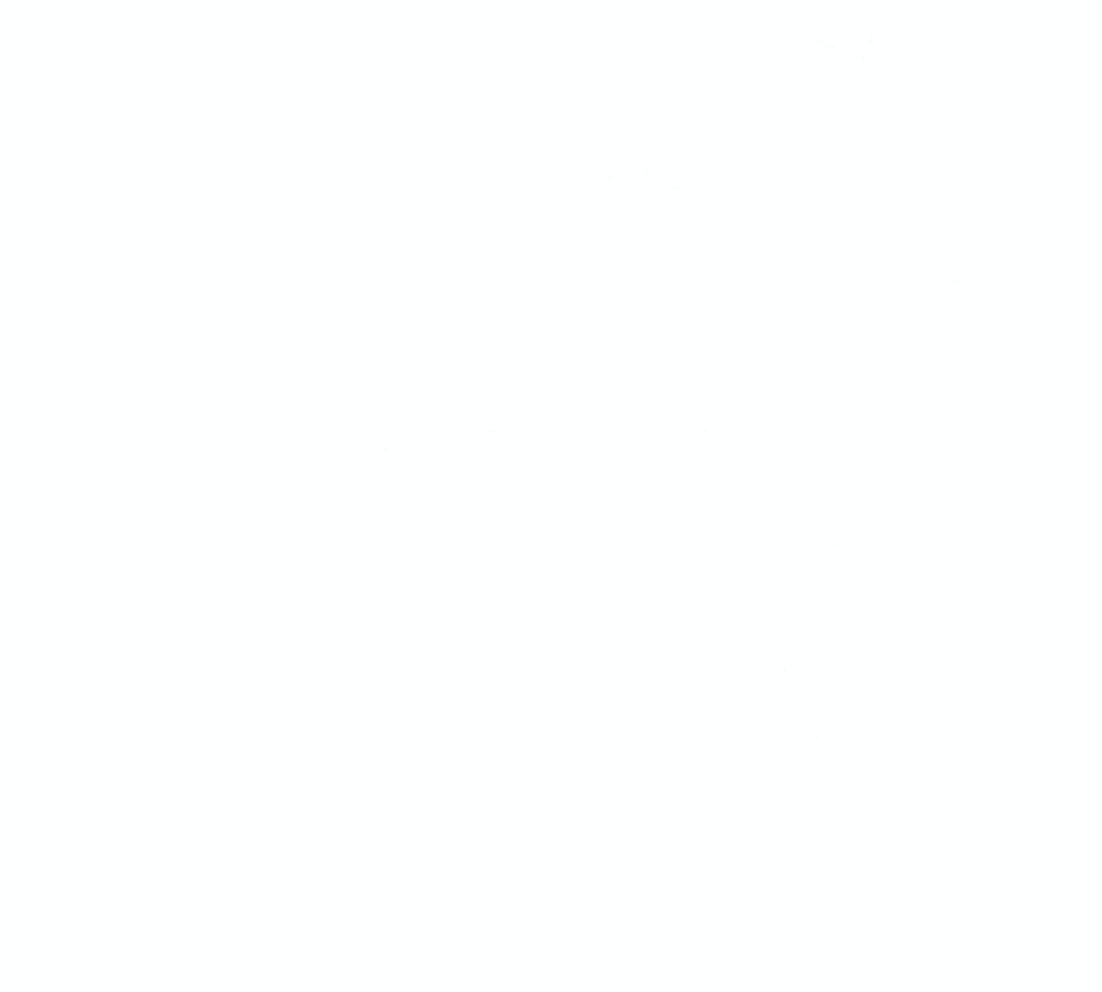
IPFormer: Visual 3D Panoptic Scene Completion with Context-Adaptive Instance Proposals
IPFormer is the first method that leverages context-adaptive instance proposals at train and test time to address vision-based 3D Panoptic Scene Completion. Specifically, IPFormer adaptively initializes these queries as panoptic instance proposals derived from image context and further refines them through attention-based encoding and decoding to reason about semantic instance-voxel relationships.
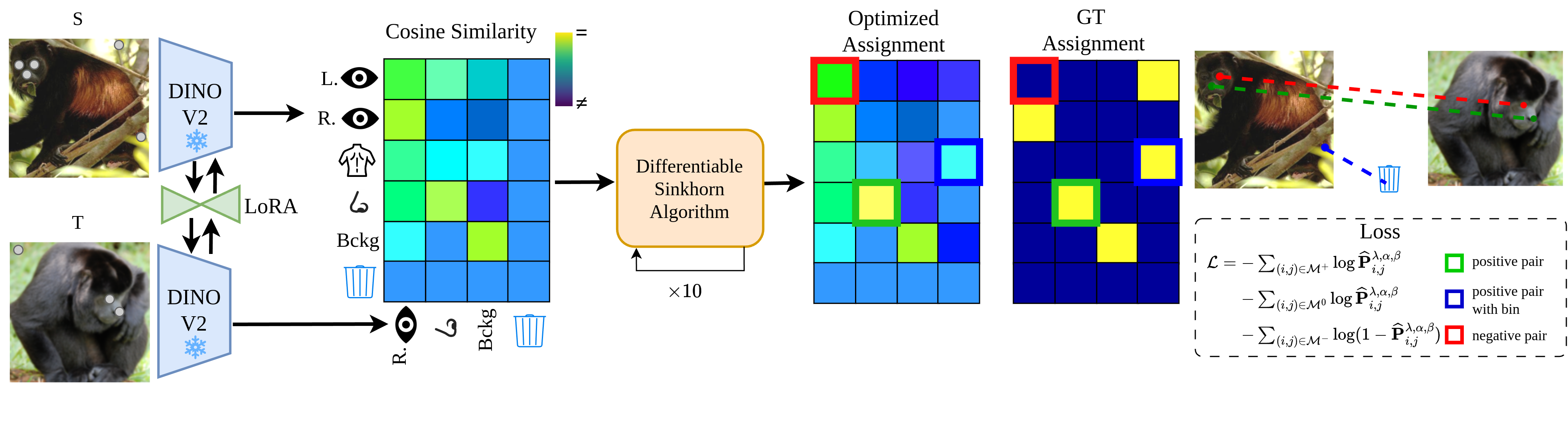
GECO: Geometrically Consistent Embedding with Lightspeed Inference
A novel, optimal-transport based learning method to solve the challenge of matching semantically similar parts distinguished by their geometric properties, e.g., left/right eyes or front/back legs. It is faster and outperforms previous supervised methods in terms of semantic matching and geometric understanding.
Dream-to-Recon: Monocular 3D Reconstruction with Diffusion-Depth Distillation from Single Images
We leverage a diffusion model and a depth predictor to generate high-quality scene geometry from a single image. Then, we distill a feed-forward scene reconstruction model, which performs on par with methods trained via multi-view supervision.
AnyCam: Learning to Recover Camera Poses and Intrinsics from Casual Videos
AnyCam is a fast transformer model that directly estimates camera poses and intrinsics from a dynamic video sequence in feed-forward fashion. This network can learn strong priors over realistic camera motion, by training on diverse, unlabelled video datasets obtained mostly from YouTube.
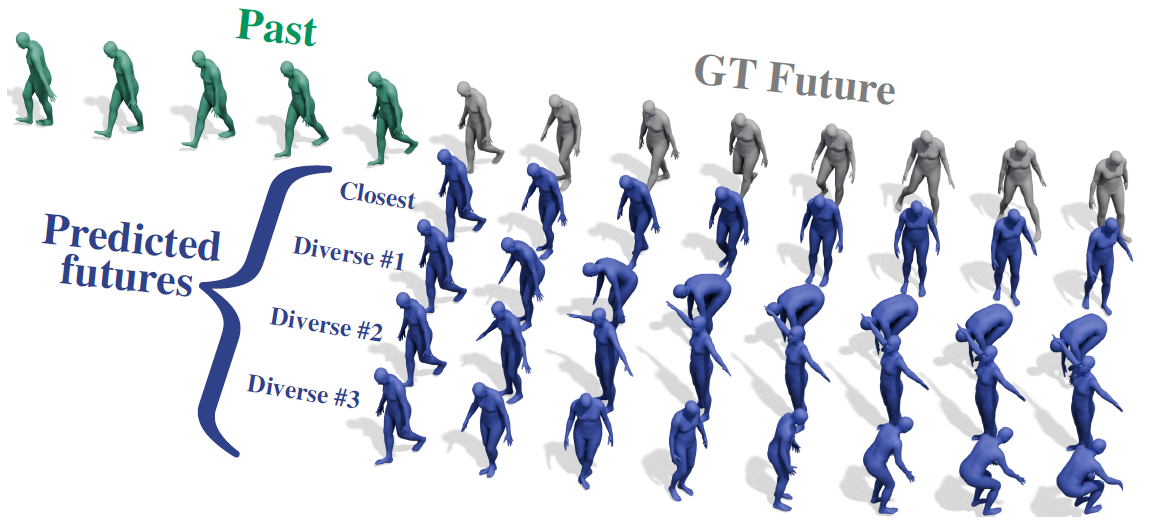
Nonisotropic Gaussian Diffusion for Realistic 3D Human Motion Prediction
SkeletonDiffusion is a novel nonisotropic diffusion approach for 3D Human Motion Prediction, and the first computer vision method to show to use nonisotropic diffusion. We generate diverse and realistic motions achieving state-of-the-art performance.
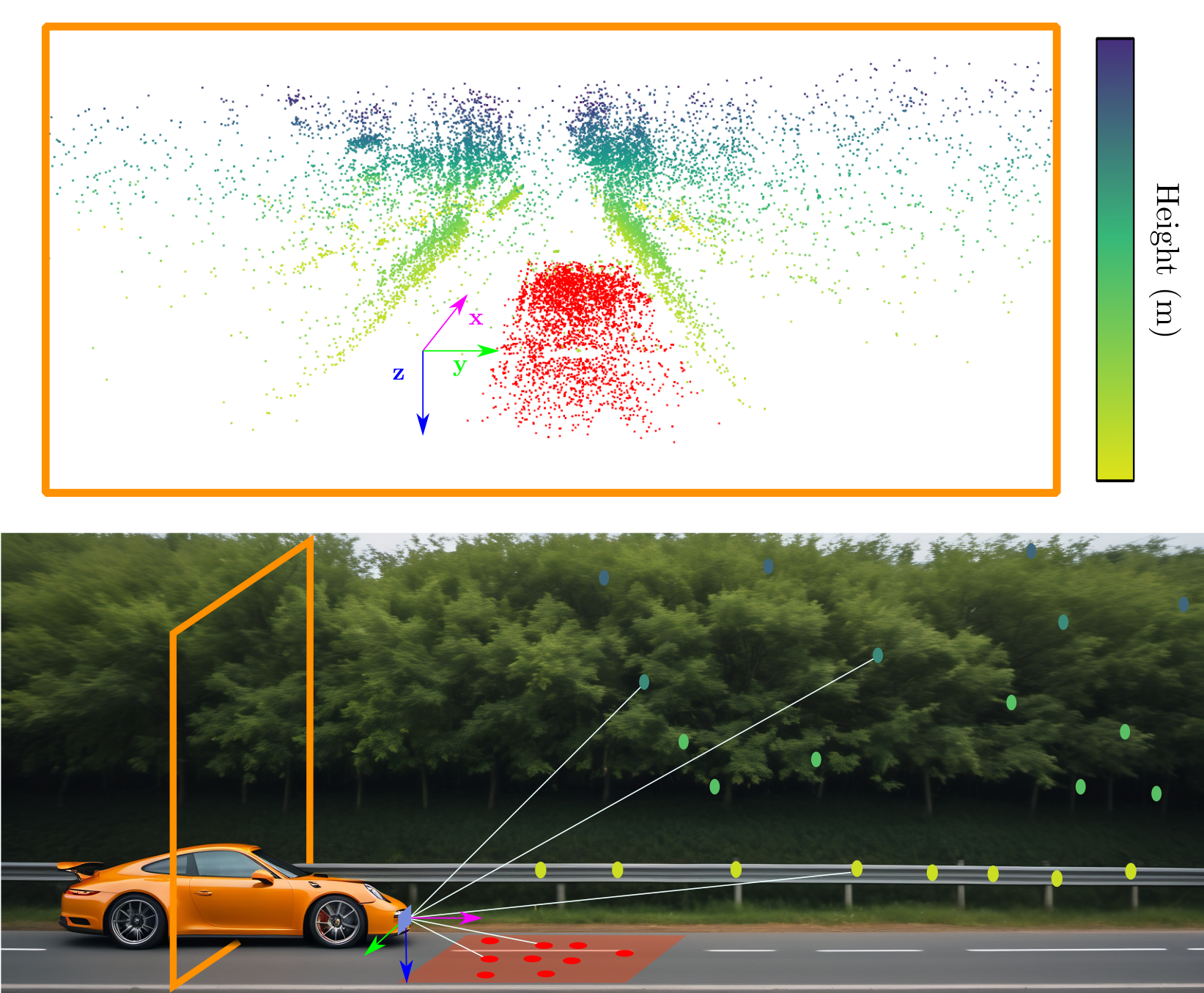
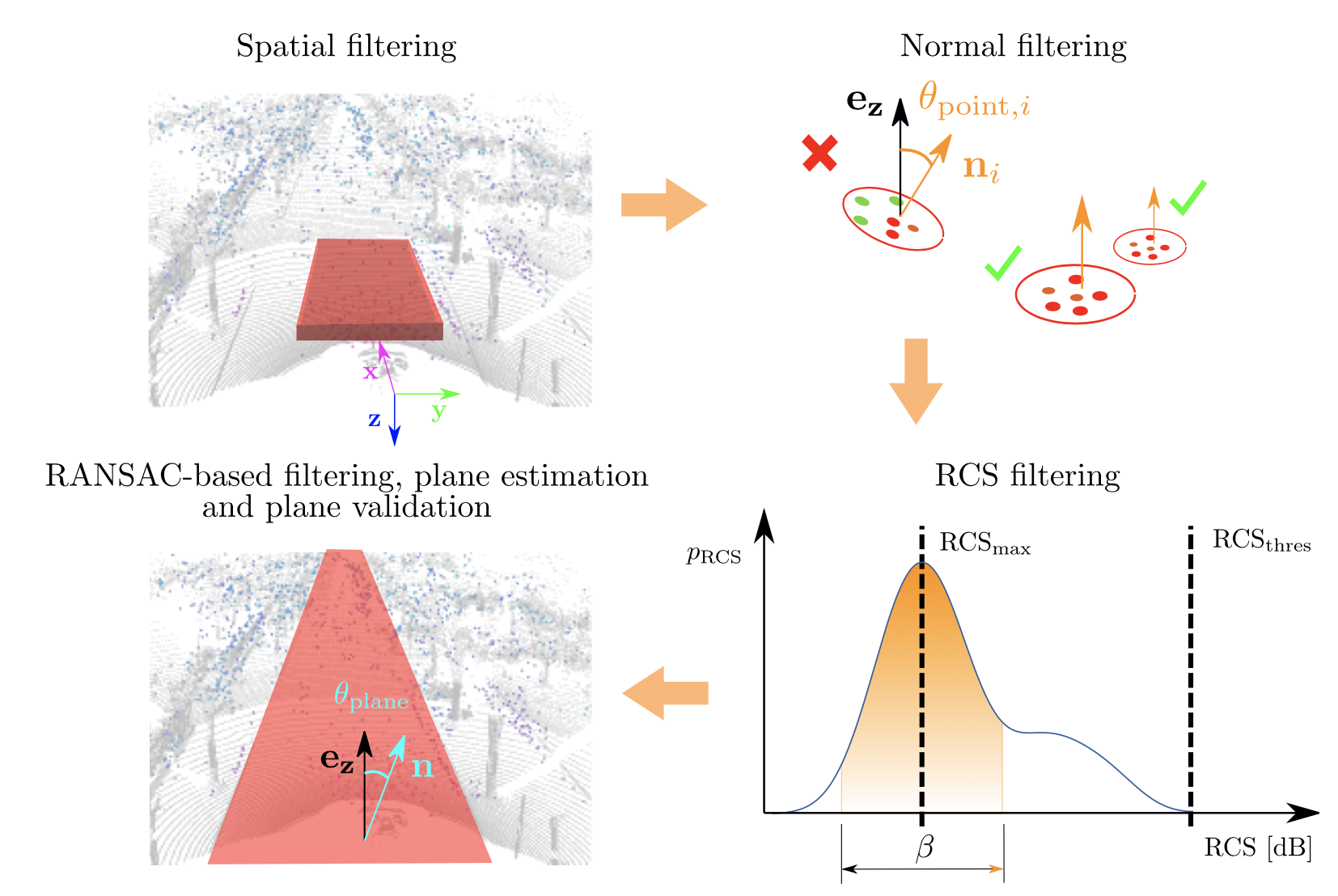
Ground-Aware Automotive Radar Odometry
We propose a simple, yet effective, heuristic-based method to extract the ground plane from single radar scans and perform ground plane matching between consecutive scan.
Gaussian Splatting in Style
We are the first to employ Gaussian Splatting to solve the task of scene stylization, extending the work of neural style transfer to three spatial dimensions.
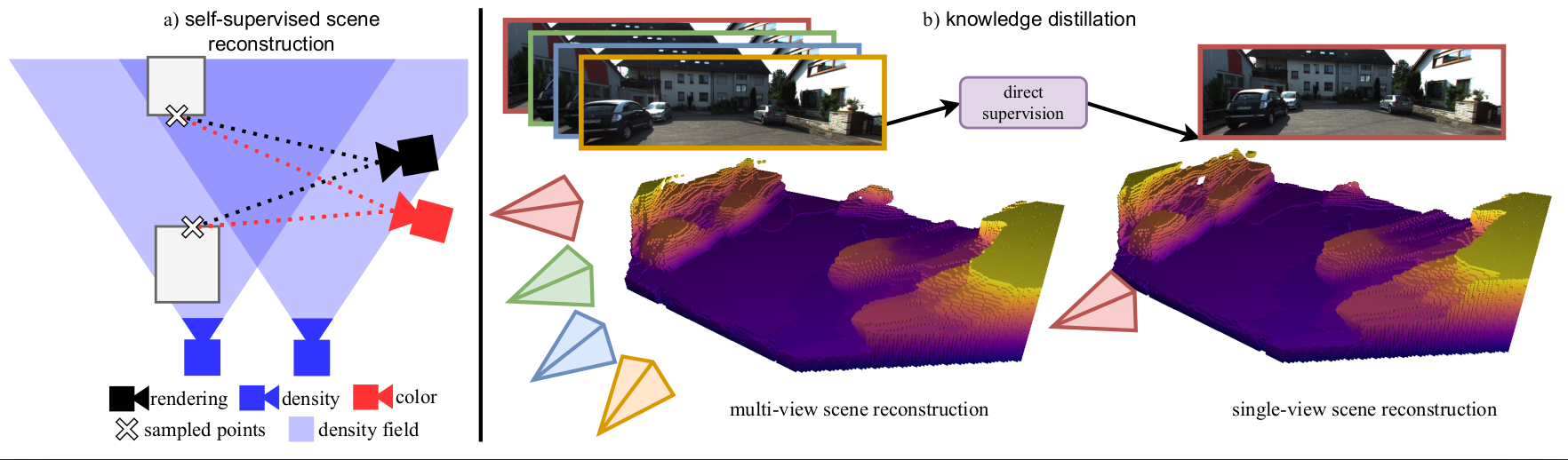
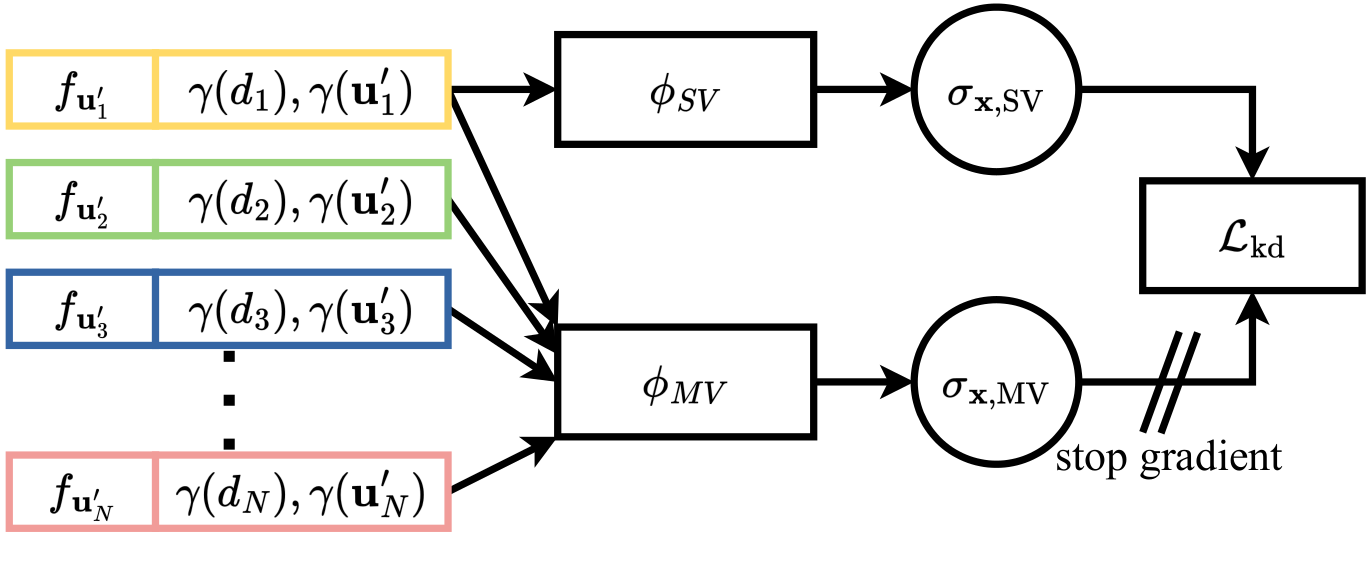
Boosting Self-Supervision for Single View Scene Completion via Knowledge Distillation
We use multi-view scene completion to supervise single-view scene completion and boost its performance. We propose both a novel multi-view scene completion network and a corresponding knowledge distillation scheme.
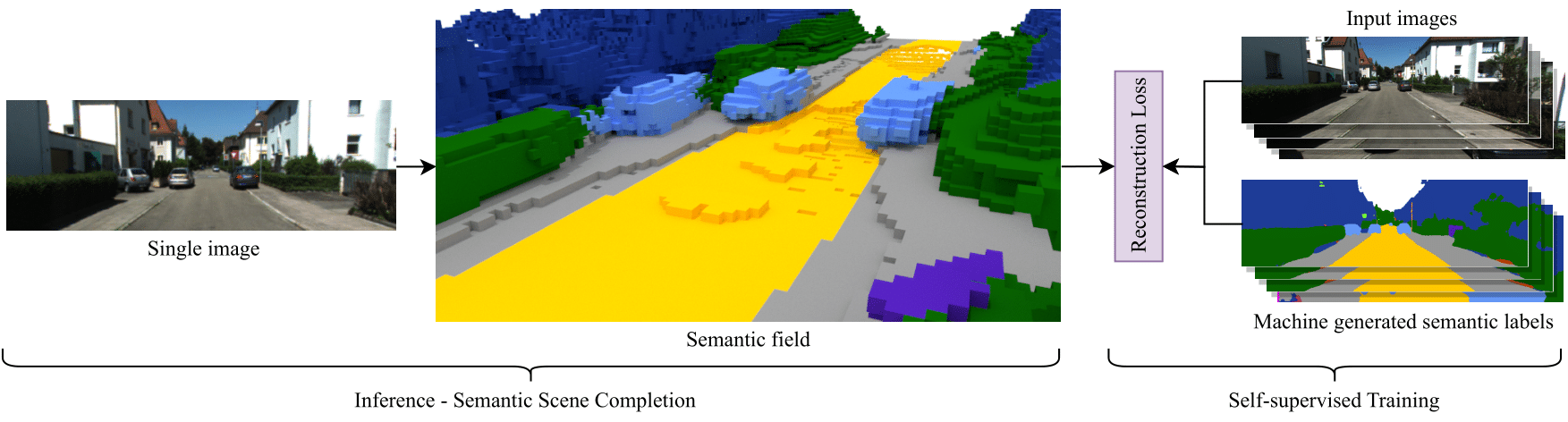
S4C: Self-Supervised Semantic Scene Completion with Neural Fields
S4C is the first self-supervised approach to the Sematic Scence Completion task. It achives close to state-of-the-art performance on the KITTI-360 SSCBench dataset.
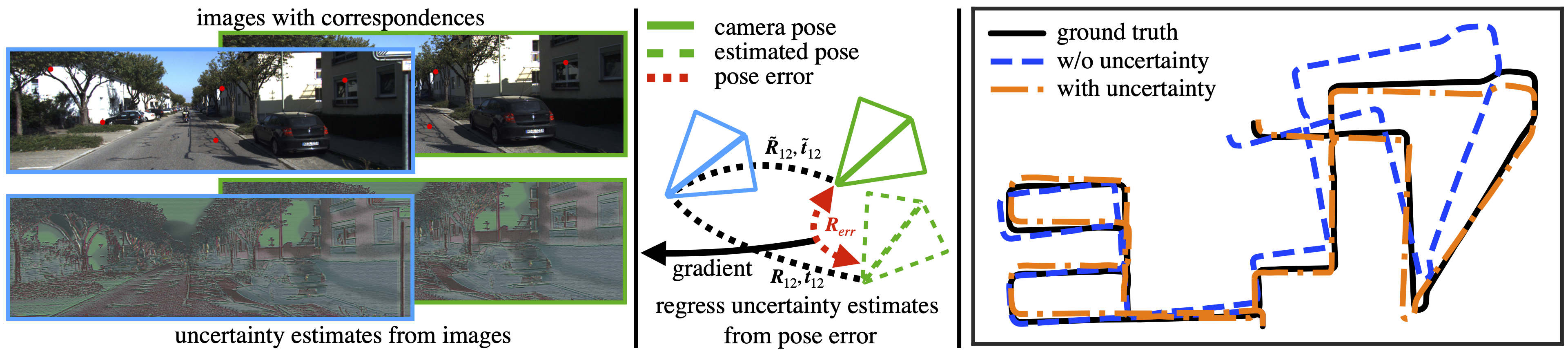
Learning Correspondence Uncertainty via Differentiable Nonlinear Least Squares
A differentiable nonlinear least squares framework to account for uncertainty in relative pose estimation from feature correspondences regardless of the feature extraction algorithm of choice.
Probabilistic Normal Epipolar Constraint for Frame-To-Frame Rotation Optimization under Uncertain Feature Positions
We propose a probabilistic extension to the normal epipolar constraint (NEC) which we call the PNEC. It allows to account for keypoint position uncertainty in images to produce more accurate frame to frame pose estimates.